Heavy-light Decomposition With Globally Balanced Binary Trees
Table Of Contents
Prerequisite
- Segment tree - Tutorial on cp-algorithms
- Heavy-light decomposition - Tutorial on cp-algorithms
Introduction
안녕하세요, Aeren입니다! 다음 문제를 생각해봅시다.
Monoid $(T,+)$와 $(L,+)$, left monoid action $\ast(\ast):(L,T)\rightarrow T$, tree $G=(V,E)$와 각 node의 가중치 $W:V\rightarrow T$이 주어진다. 다음 연산들을 수행하라.
- $u,v\in V$이 주어진다. $u$와 $v$를 잇는 유일한 path $P$에 대하여 $\sum_{w\in P}W(w)$의 값을 출력한다.
- $u,v\in V$와 $f\in L$이 주어진다. $u$와 $v$를 잇는 유일한 path $P$에 대하여 각 $w\in P$에 대해 $W(w)$의 값을 $f(W(w))$로 바꾼다.
위 연산들은 heavy-light decomposition과 segment tree로 간단한 구현으로 $O(\vert V\vert)$시간의 전처리로 $O(\log^2\vert V\vert)$시간 안에 처리할 수 있음이 알려져 있습니다.
그런데 link-cut tree라는 자료구조를 이용하면 (이 자료구조를 몰라도 이 글을 이해하는데는 큰 지장이 없습니다.) 똑같은 전처리 시간으로 amortized $O(\log\vert V\vert)$시간 안에 위 연산들을 처리할 수 있습니다. 그리고 이 자료구조는 추가로 “서로다른 component에 edge 삽입” / “edge 삭제”등의 연산을 지원합니다.
자료구조를 공부해 본 분이라면 더 많은 연산을 지원할수록 연산이 더 무거워 지는 경향이 있다는 것을 아실 것입니다. Link-cut tree도 역시 dynamic graph 연산을 지원하기에 각 연산에 붙는 상수가 매우 크며, 구현 난이도 또한 상당합니다.
이 글에서 다룰 자료구조는 위 두 자료구조의 “중간지점”입니다. 즉, 상수 및 구현난이도를 작게 유지하면서 $O(\log \vert V\vert)$의 시간복잡도로 위 연산들을 처리하는 것이 목표입니다.
Main Idea
일단 heavy-light decomposition + segment tree풀이를 살펴보겠습니다. Heavy-light decomposition은 $G$를 long chain들의 disjoint union으로 분할하며 임의의 node $u$와 $v$에 대해서 $u-v$ path는 각각의 long chain들과의 intersection으로 부터 $ O( \log \vert V \vert) $개의 non-empty chain으로 쪼개집니다. 이제 $ G $에 대한 dfs ordering 위에서 segment tree를 만들면 각각의 long chain들은 연속된 구간으로 나타나므로 각각의 chain들은 $O(\log\vert V\vert)$시간에 update / query 할 수 있게 되고 총 시간복잡도는 $O(\log^2\vert V\vert)$입니다.
Segment tree는 주어진 구간을 balanced binary tree로 쪼개어 구간 연산을 빠르게 처리하게 해주는 자료구조입니다. 즉, 잘 생각해보면, link-cut tree가 amortized $O(\log\vert V\vert)$에 지원하는 연산이 이 방법으로는 하나의 $\log$가 더 붙는 이유는 segment tree가 주어진 dfs ordering의 “local balancing”만 고려하기 때문입니다. 핵심 아이디어는 이 “local balancing”을 “global balancing”으로 바꿔주는 것입니다.
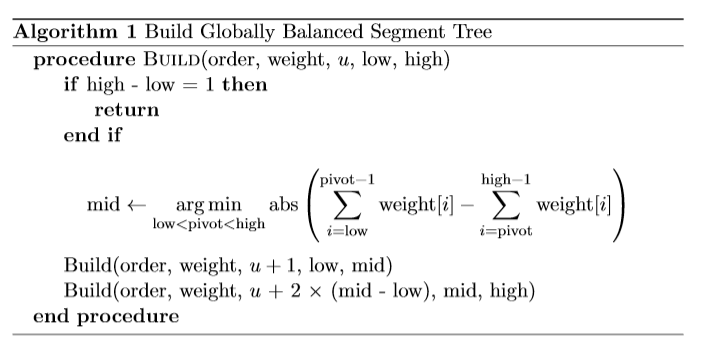
주어진 dfs ordering $\textrm{order}$에 대해서 $\textrm{weight}$배열을 $\textrm{weight}[i]=1+\sum_{u\in \textrm{light_child}[\textrm{order}[i]]}\textrm{subtree_size}[u]$이라 정의합시다. 그리고 long chain위에서 binary tree를 만들 때 구간 $[l,r)$을 쪼개는 지점을 $(l+r)/2$가 아닌 $ \textrm{argmin} _ {l<m<r}( \textrm{abs}( \sum _ {i=l}^{m-1} \textrm{weight}[i]- \sum _ {i=m}^{r-1} \textrm{weight}[i])) $으로 두겠습니다. 이제 각 update / query에서 고려되는 node들은 높이가 감소하는 순서대로 볼 때, 1. $\textrm{weight}[u]$가 절반으로 줄던지, 혹은 2. light edge를 타고 내려오게 됩니다. 즉, 전체 시간복잡도가 $O(\log\vert V\vert)$임을 얻을 수 있습니다. (이 방법은 link-cut tree에서 같은 시간복잡도를 얻어내는 방법과 매우 유사합니다.)
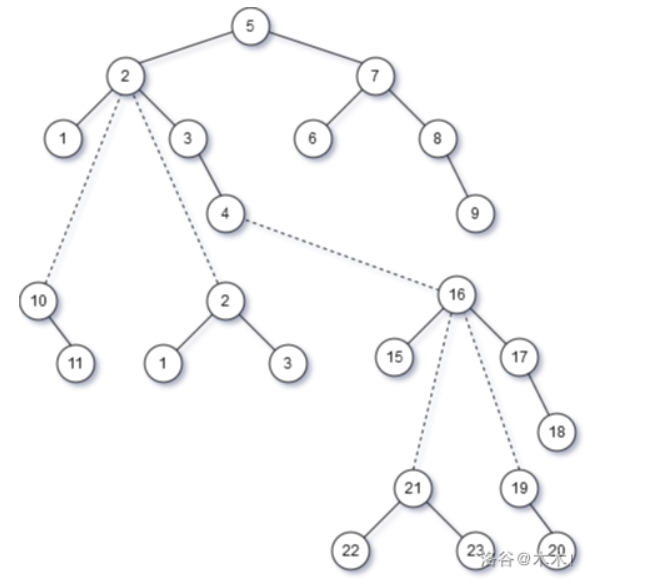
아래 예시에서 (이미지 출처는 여기입니다.) 위 이미지는 heavy-light decomposition에서 locally balanced binary tree를 만들었을 때, 아래는 globally balanced binary tree를 만들었을 때를 보여줍니다. (점선으로 된 edge들은 시간복잡도 분석을 위해 첨가되었습니다.)
Globally balanced binary tree들을 만들었을 때 전체 자료구조가 더 balanced해짐을 눈으로 확인할 수 있습니다.
Implementation
Dfs ordering과 $\textrm{weight}$배열이 주어졌을 때 globally balanced binary tree는 다음과 같이 구현할 수 있습니다.
각 long chain에 대해 dfs ordering이 [low, high)의 구간을 갖는다면 $\textrm{build}(\textrm{order}, \textrm{weight}, u, \textrm{low}, \textrm{high})$를 호출하면 $u$를 root로 하는 globally balanced segment tree가 생성됩니다.
Benchmark
다음은 perfect binary tree에서 랜덤한 leaf node 쌍의 update / query 가 주어질 때 시행시간을 표로 정리한 것입니다.
HLD + locally / globally balanced binary trees runtime comparison (in seconds). Bolded indicates faster.
| $\vert V\vert\,\backslash \, Q$ | $2^{16}-1$ | $2^{18}-1$ | $2^{20}-1$ |
|---|---|---|---|
| $2^{16}-1$ | 0.44/0.20 | 1.60/0.62 | 6.38/2.31 |
| $2^{18}-1$ | 0.75/0.40 | 2.55/1.05 | 9.60/3.71 |
| $2^{20}-1$ | 1.49/1.13 | 3.89/2.30 | 14.34/6.28 |
다음은 위 데이터를 얻는데 사용한 C++ 코드입니다.
Generator
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace chrono;
mt19937 rng(high_resolution_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());
int main(){
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.exceptions(ios::badbit | ios::failbit);
const int nbit = /*14, 16, */20, qbit = /*14, 16, */20;
int n = (1 << nbit) - 1, qn = (1 << qbit) - 1, mx = 1e5;
cout << n << "\n";
for(auto u = 1; 2 * u + 1 <= n; ++ u){
cout << u << " " << 2 * u << "\n";
cout << u << " " << 2 * u + 1 << "\n";
}
cout << qn << "\n";
for(auto qi = 0; qi < qn; ++ qi){
int u = rng() % (n / 2 + 1) + n / 2 + 1;
int v = rng() % (n / 2 + 1) + n / 2 + 1;
if(rng() & 1){
cout << "1 " << u << " " << v << " " << rng() % mx + 1 << "\n";
}
else{
cout << "2 " << u << " " << v << "\n";
}
}
return 0;
}
Locally Balanced
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
struct graph{
struct edge{
int from, to;
T cost;
};
int n;
vector<edge> edges;
vector<vector<int>> adj;
function<bool(int)> ignore;
graph(int n): n(n), adj(n){ }
int link(int u, int v, T w = {}){ // insert an undirected edge
int id = (int)edges.size();
adj[u].push_back(id), adj[v].push_back(id), edges.push_back({u, v, w});
return id;
}
int orient(int u, int v, T w = {}){ // insert a directed edge
int id = (int)edges.size();
adj[u].push_back(id), edges.push_back({u, v, w});
return id;
}
graph transposed() const{ // the transpose of the directed graph
graph res(n);
for(auto &e: edges) res.orient(e.to, e.from, e.cost);
res.ignore = ignore;
return res;
}
int degree(int u) const{ // the degree (outdegree if directed) of u (without the ignoration rule)
return (int)adj[u].size();
}
vector<vector<int>> get_adjacency_list() const{
vector<vector<int>> res(n);
for(auto u = 0; u < n; ++ u) for(auto id: adj[u]){
if(ignore && ignore(id)) continue;
auto &e = edges[id];
int v = u ^ e.from ^ e.to;
res[u].push_back(v);
}
return res;
}
void set_ignoration_rule(const function<bool(int)> &f){
ignore = f;
}
void reset_ignoration_rule(){
ignore = nullptr;
}
};
// Requires graph
template<int VALS_IN_EDGES = 0>
struct heavy_light_decomposition{
int n;
vector<vector<int>> adj;
vector<int> roots; // root of the component
vector<int> pv;
vector<int> pe;
vector<int> sz;
vector<int> depth;
vector<int> next; // highest point of the heavy path
vector<int> pos;
vector<int> end;
vector<int> order;
template<class T>
heavy_light_decomposition(const graph<T> &g, const vector<int> &roots): n(g.n), roots(roots), adj(n), pv(n, -1), pe(n, -1), sz(n, 1), depth(n), next(n), pos(n), end(n){
for(auto id = 0; id < (int)g.edges.size(); ++ id){
if(g.ignore && g.ignore(id)) continue;
auto &e = g.edges[id];
adj[e.from].push_back(id), adj[e.to].push_back(id);
}
auto dfs_init = [&](auto dfs_init, int u, int root)->void{
next[u] = root;
if(~pe[u]) adj[u].erase(find(adj[u].begin(), adj[u].end(), pe[u]));
for(auto &id: adj[u]){
auto &e = g.edges[id];
int v = u ^ e.from ^ e.to;
pv[v] = u, pe[v] = id, depth[v] = depth[u] + 1;
dfs_init(dfs_init, v, u);
sz[u] += sz[v];
auto &f = g.edges[adj[u][0]];
if(sz[v] > sz[u ^ f.from ^ f.to]) swap(id, adj[u][0]);
}
};
int timer = 0;
auto dfs_hld = [&](auto dfs_hld, int u)->void{
pos[u] = timer ++;
order.push_back(u);
if(!adj[u].empty()){
auto &f = g.edges[adj[u][0]];
int hv = u ^ f.from ^ f.to;
for(auto id: adj[u]){
auto &e = g.edges[id];
int v = u ^ e.from ^ e.to;
next[v] = (v == hv ? next[u] : v);
dfs_hld(dfs_hld, v);
}
}
end[u] = timer;
};
for(auto r: roots) assert(!~pv[r]), dfs_init(dfs_init, r, r), dfs_hld(dfs_hld, r);
}
int lca(int u, int v){
for(; next[u] != next[v]; v = pv[next[v]]) if(depth[next[u]] > depth[next[v]]) swap(u, v);
return depth[u] < depth[v] ? u : v;
}
int steps(int u, int v, int w = -1){
return depth[u] + depth[v] - 2 * depth[~w ? w : lca(u, v)];
}
// f reads the position in the data structure
void querynode(int u, auto f){ f(pos[u]); } // one application of f
void querysubtree(int u, auto f){ f(pos[u] + VALS_IN_EDGES, end[u]); } // one application of f
void querypath(int u, int v, auto f){ // reads left, right, (left->right ?), O(log N) applications of f
bool dir = true;
for(; next[u] != next[v]; v = pv[next[v]]){
if(depth[next[u]] > depth[next[v]]) swap(u, v), dir = !dir;
f(pos[next[v]], pos[v] + 1, dir);
}
if(depth[u] > depth[v]) swap(u, v), dir = !dir;
f(pos[u] + VALS_IN_EDGES, pos[v] + 1, dir);
}
auto getpath(int u, int v){ // O(log N)
vector<pair<int, int>> resl, resr; // pair of indices {l, r} in the data structure; resr is reversed(v->next[v], pv[next[v]]-> ...)
querypath(u, v, [&](int l, int r, bool dir){ (dir ? resl : resr).push_back({l, r}); });
return pair{resl, resr};
}
};
template<class T, class U, class F1, class F2, class F3, class F4>
struct recursive_segment_tree{
int n;
vector<T> data;
vector<U> updates;
F1 TT; // monoid operation (always adjacent)
T T_id; // monoid identity
F2 UU; // semigroup operation (superset, subset)
F3 U_init; // semigroup default element for the interval [l, r)
F4 UT; // action of U on T (superset, subset)
recursive_segment_tree(int n, F1 TT, T T_id, F2 UU, F3 U_init, F4 UT): recursive_segment_tree(vector<T>(n, T_id), TT, T_id, UU, U_init, UT){ }
recursive_segment_tree(int n, T init, F1 TT, T T_id, F2 UU, F3 U_init, F4 UT): recursive_segment_tree(vector<T>(n, init), TT, T_id, UU, U_init, UT){ }
recursive_segment_tree(const vector<T> &a, F1 TT, T T_id, F2 UU, F3 U_init, F4 UT): n((int)a.size()), data(n << 1, T_id), updates(n << 1), TT(TT), T_id(T_id), UU(UU), U_init(U_init), UT(UT){
build(a, 0, 0, n);
}
void build(const vector<T> &a, int u, int l, int r){
if(l + 1 == r) data[u] = a[l], updates[u] = U_init(l, r);
else{
int m = l + (r - l >> 1), v = u + 1, w = u + (m - l << 1);
build(a, v, l, m), build(a, w, m, r);
data[u] = TT(data[v], data[w]), updates[u] = U_init(l, r);
}
}
void push(int u, int l, int r){ // push the internal node u
int m = l + (r - l >> 1), v = u + 1, w = u + (m - l << 1);
data[v] = UT(updates[u], data[v]);
updates[v] = UU(updates[u], updates[v]);
data[w] = UT(updates[u], data[w]);
updates[w] = UU(updates[u], updates[w]);
updates[u] = U_init(l, r);
}
void refresh(int u, int l, int r){
data[u] = UT(updates[u], TT(data[u + 1], data[u + (r - l >> 1 << 1)]));
}
void update(int ql, int qr, U x){ // Apply x to values at [ql, qr)
auto recurse = [&](auto recurse, int u, int l, int r)->void{
if(qr <= l || r <= ql) return;
if(ql <= l && r <= qr){
data[u] = UT(x, data[u]), updates[u] = UU(x, updates[u]);
return;
}
push(u, l, r);
int m = l + (r - l >> 1);
recurse(recurse, u + 1, l, m), recurse(recurse, u + (m - l << 1), m, r);
refresh(u, l, r);
};
recurse(recurse, 0, 0, n);
}
T query(int ql, int qr){ // Get the query result for [ql, qr)
auto recurse = [&](auto recurse, int u, int l, int r)->T{
if(qr <= l || r <= ql) return T_id;
if(ql <= l && r <= qr) return data[u];
push(u, l, r);
int m = l + (r - l >> 1);
return TT(recurse(recurse, u + 1, l, m), recurse(recurse, u + (m - l << 1), m, r));
};
return recurse(recurse, 0, 0, n);
}
};
int main(){
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.exceptions(ios::badbit | ios::failbit);
int n;
cin >> n;
graph<int> g(n);
for(auto i = 0; i < n - 1; ++ i){
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v, -- u, -- v;
g.link(u, v);
}
heavy_light_decomposition hld(g, {0});
using T = pair<int, long long>;
auto TT = [&](T x, T y){
return T{x.first + y.first, x.second + y.second};
};
T T_id = {0, 0};
auto U_init = [&](int l, int r){
return 0LL;
};
auto act = [&](long long f, T x){
return T{x.first, x.second + x.first * f};
};
vector<T> a(n, {1, 0});
recursive_segment_tree<T, long long, decltype(TT), plus<>, decltype(U_init), decltype(act)>
ds(vector<T>(n, {1, 0}), TT, T_id, plus<>(), U_init, act);
int qn;
cin >> qn;
for(auto qi = 0; qi < qn; ++ qi){
int type, u, v;
cin >> type >> u >> v, -- u, -- v;
if(type == 1){
int x;
cin >> x;
hld.querypath(u, v, [&](int l, int r, bool){ ds.update(l, r, x); });
}
else{
long long sum = 0;
hld.querypath(u, v, [&](int l, int r, bool){ sum += ds.query(l, r).second; });
cout << sum << "\n";
}
}
return 0;
}
Globally Balanced
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
struct graph{
struct edge{
int from, to;
T cost;
};
int n;
vector<edge> edges;
vector<vector<int>> adj;
function<bool(int)> ignore;
graph(int n): n(n), adj(n){ }
int link(int u, int v, T w = {}){ // insert an undirected edge
int id = (int)edges.size();
adj[u].push_back(id), adj[v].push_back(id), edges.push_back({u, v, w});
return id;
}
int orient(int u, int v, T w = {}){ // insert a directed edge
int id = (int)edges.size();
adj[u].push_back(id), edges.push_back({u, v, w});
return id;
}
graph transposed() const{ // the transpose of the directed graph
graph res(n);
for(auto &e: edges) res.orient(e.to, e.from, e.cost);
res.ignore = ignore;
return res;
}
int degree(int u) const{ // the degree (outdegree if directed) of u (without the ignoration rule)
return (int)adj[u].size();
}
vector<vector<int>> get_adjacency_list() const{
vector<vector<int>> res(n);
for(auto u = 0; u < n; ++ u) for(auto id: adj[u]){
if(ignore && ignore(id)) continue;
auto &e = edges[id];
int v = u ^ e.from ^ e.to;
res[u].push_back(v);
}
return res;
}
void set_ignoration_rule(const function<bool(int)> &f){
ignore = f;
}
void reset_ignoration_rule(){
ignore = nullptr;
}
};
// Requires graph
template<int VALS_IN_EDGES = 0>
struct heavy_light_decomposition{
int n;
vector<vector<int>> adj;
vector<int> roots; // root of the component
vector<int> pv;
vector<int> pe;
vector<int> sz;
vector<int> depth;
vector<int> next; // highest point of the heavy path
vector<int> pos;
vector<int> end;
vector<int> order;
template<class T>
heavy_light_decomposition(const graph<T> &g, const vector<int> &roots): n(g.n), roots(roots), adj(n), pv(n, -1), pe(n, -1), sz(n, 1), depth(n), next(n), pos(n), end(n){
for(auto id = 0; id < (int)g.edges.size(); ++ id){
if(g.ignore && g.ignore(id)) continue;
auto &e = g.edges[id];
adj[e.from].push_back(id), adj[e.to].push_back(id);
}
auto dfs_init = [&](auto dfs_init, int u, int root)->void{
next[u] = root;
if(~pe[u]) adj[u].erase(find(adj[u].begin(), adj[u].end(), pe[u]));
for(auto &id: adj[u]){
auto &e = g.edges[id];
int v = u ^ e.from ^ e.to;
pv[v] = u, pe[v] = id, depth[v] = depth[u] + 1;
dfs_init(dfs_init, v, u);
sz[u] += sz[v];
auto &f = g.edges[adj[u][0]];
if(sz[v] > sz[u ^ f.from ^ f.to]) swap(id, adj[u][0]);
}
};
int timer = 0;
auto dfs_hld = [&](auto dfs_hld, int u)->void{
pos[u] = timer ++;
order.push_back(u);
if(!adj[u].empty()){
auto &f = g.edges[adj[u][0]];
int hv = u ^ f.from ^ f.to;
for(auto id: adj[u]){
auto &e = g.edges[id];
int v = u ^ e.from ^ e.to;
next[v] = (v == hv ? next[u] : v);
dfs_hld(dfs_hld, v);
}
}
end[u] = timer;
};
for(auto r: roots) assert(!~pv[r]), dfs_init(dfs_init, r, r), dfs_hld(dfs_hld, r);
}
int lca(int u, int v){
for(; next[u] != next[v]; v = pv[next[v]]) if(depth[next[u]] > depth[next[v]]) swap(u, v);
return depth[u] < depth[v] ? u : v;
}
int steps(int u, int v, int w = -1){
return depth[u] + depth[v] - 2 * depth[~w ? w : lca(u, v)];
}
// f reads the position in the data structure
void querynode(int u, auto f){ f(pos[u]); } // one application of f
void querysubtree(int u, auto f){ f(pos[u] + VALS_IN_EDGES, end[u]); } // one application of f
void querypath(int u, int v, auto f){ // reads left, right, (left->right ?), O(log N) applications of f
bool dir = true;
for(; next[u] != next[v]; v = pv[next[v]]){
if(depth[next[u]] > depth[next[v]]) swap(u, v), dir = !dir;
f(pos[next[v]], pos[v] + 1, dir);
}
if(depth[u] > depth[v]) swap(u, v), dir = !dir;
f(pos[u] + VALS_IN_EDGES, pos[v] + 1, dir);
}
auto getpath(int u, int v){ // O(log N)
vector<pair<int, int>> resl, resr; // pair of indices {l, r} in the data structure; resr is reversed(v->next[v], pv[next[v]]-> ...)
querypath(u, v, [&](int l, int r, bool dir){ (dir ? resl : resr).push_back({l, r}); });
return pair{resl, resr};
}
};
template<class T, class U, class F1, class F2, class F3, class F4>
struct weighted_lazy_segment_tree{
int n;
vector<T> data;
vector<U> updates;
vector<int> root, m;
vector<array<int, 2>> range;
F1 TT; // monoid operation (always adjacent)
T T_id; // monoid identity
F2 UU; // semigroup operation (superset, subset)
F3 U_init; // semigroup default element for the interval [l, r)
F4 UT; // action of U on T (superset, subset)
weighted_lazy_segment_tree(int n, const vector<int> &partition, const vector<int> &weights, F1 TT, T T_id, F2 UU, F3 U_init, F4 UT): weighted_lazy_segment_tree(vector<T>(n, T_id), partition, weights, TT, T_id, UU, U_init, UT){ }
weighted_lazy_segment_tree(int n, const vector<int> &partition, const vector<int> &weights, T init, F1 TT, T T_id, F2 UU, F3 U_init, F4 UT): weighted_lazy_segment_tree(vector<T>(n, init), partition, weights, TT, T_id, UU, U_init, UT){ }
weighted_lazy_segment_tree(const vector<T> &a, const vector<int> &partition, const vector<int> &weights, F1 TT, T T_id, F2 UU, F3 U_init, F4 UT): n((int)a.size()), data(n << 1, T_id), updates(n << 1), root(n + 1), range(n + 1), m(n << 1), TT(TT), T_id(T_id), UU(UU), U_init(U_init), UT(UT){
vector<long long> pref(n + 1);
for(auto i = 0; i < n; ++ i) pref[i + 1] = pref[i] + weights[i];
assert(accumulate(partition.begin(), partition.end(), 0) == n);
int u = 0, l = 0, r = 0;
for(auto len: partition){
assert(len >= 1);
r += len;
for(auto i = l; i < r; ++ i) root[i] = u, range[i] = {l, r};
build(a, pref, u, l, r);
u += 2 * len - 1, l = r;
}
root[l] = u;
range[n] = {l, l};
}
void build(const vector<T> &a, const vector<long long> &pref, int u, int l, int r){
if(l + 1 == r) data[u] = a[l], updates[u] = U_init(l, r);
else{
m[u] = partition_point(pref.begin() + (l + 1), pref.begin() + (r - 1), [&](auto x){ return x - pref[l] < pref[r] - x; }) - pref.begin();
assert(l < m[u] && m[u] < r);
int v = u + 1, w = u + (m[u] - l << 1);
build(a, pref, v, l, m[u]), build(a, pref, w, m[u], r);
data[u] = TT(data[v], data[w]), updates[u] = U_init(l, r);
}
}
void push(int u, int l, int r){ // push the internal node u
int v = u + 1, w = u + (m[u] - l << 1);
data[v] = UT(updates[u], data[v]);
updates[v] = UU(updates[u], updates[v]);
data[w] = UT(updates[u], data[w]);
updates[w] = UU(updates[u], updates[w]);
updates[u] = U_init(l, r);
}
void refresh(int u, int l, int r){
data[u] = UT(updates[u], TT(data[u + 1], data[u + (m[u] - l << 1)]));
}
void set(int p, T x){
auto recurse = [&](auto recurse, int u, int l, int r)->void{
if(p < l || r <= p) return;
if(p == l && p + 1 == r){
data[u] = x, updates[u] = U_init(l, r);
return;
}
push(u, l, r);
recurse(recurse, u + 1, l, m[u]), recurse(recurse, u + (m[u] - l << 1), m[u], r);
refresh(u, l, r);
};
recurse(recurse, root[p], range[p][0], range[p][1]);
}
void update(int p, U f){
auto recurse = [&](auto recurse, int u, int l, int r)->void{
if(p < l || r <= p) return;
if(p == l && p + 1 == r){
data[u] = UT(f, data[u]), updates[u] = UU(f, updates[u]);
return;
}
push(u, l, r);
recurse(recurse, u + 1, l, m[u]), recurse(recurse, u + (m[u] - l << 1), m[u], r);
refresh(u, l, r);
};
recurse(recurse, root[p], range[p][0], range[p][1]);
}
// assumes [ql, qr) lies within the same partition
void update(int ql, int qr, U f){ // Apply f to values at [ql, qr)
auto recurse = [&](auto recurse, int u, int l, int r)->void{
if(qr <= l || r <= ql) return;
if(ql <= l && r <= qr){
data[u] = UT(f, data[u]), updates[u] = UU(f, updates[u]);
return;
}
push(u, l, r);
recurse(recurse, u + 1, l, m[u]), recurse(recurse, u + (m[u] - l << 1), m[u], r);
refresh(u, l, r);
};
recurse(recurse, root[ql], range[ql][0], range[ql][1]);
}
// assumes [ql, qr) lies within the same partition
T query(int ql, int qr){ // Get the query result for [ql, qr)
auto recurse = [&](auto recurse, int u, int l, int r)->T{
if(qr <= l || r <= ql) return T_id;
if(ql <= l && r <= qr) return data[u];
push(u, l, r);
return TT(recurse(recurse, u + 1, l, m[u]), recurse(recurse, u + (m[u] - l << 1), m[u], r));
};
return recurse(recurse, root[ql], range[ql][0], range[ql][1]);
}
};
int main(){
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.exceptions(ios::badbit | ios::failbit);
int n;
cin >> n;
graph<int> g(n);
for(auto i = 0; i < n - 1; ++ i){
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v, -- u, -- v;
g.link(u, v);
}
heavy_light_decomposition hld(g, {0});
vector<int> partition, weights(n, 1);
vector<bool> is_head(n, true);
for(auto u = 0; u < n; ++ u){
if(g.degree(u)){
auto &e = g.edges[hld.adj[u][0]];
int v = u ^ e.from ^ e.to;
is_head[hld.pos[v]] = false;
weights[hld.pos[u]] = hld.sz[u] - hld.sz[v];
}
}
for(auto l = 0; l < n; ){
int r = find(is_head.begin() + l + 1, is_head.end(), true) - is_head.begin();
partition.push_back(r - l);
l = r;
}
using T = pair<int, long long>;
auto TT = [&](T x, T y){
return T{x.first + y.first, x.second + y.second};
};
T T_id = {0, 0};
auto U_init = [&](int l, int r){
return 0LL;
};
auto act = [&](long long f, T x){
return T{x.first, x.second + x.first * f};
};
vector<T> a(n, {1, 0});
weighted_lazy_segment_tree<T, long long, decltype(TT), plus<>, decltype(U_init), decltype(act)>
ds(vector<T>(n, {1, 0}), partition, weights, TT, T_id, plus<>(), U_init, act);
int qn;
cin >> qn;
for(auto qi = 0; qi < qn; ++ qi){
int type, u, v;
cin >> type >> u >> v, -- u, -- v;
if(type == 1){
int x;
cin >> x;
hld.querypath(u, v, [&](int l, int r, bool){ ds.update(l, r, x); });
}
else{
long long sum = 0;
hld.querypath(u, v, [&](int l, int r, bool){ sum += ds.query(l, r).second; });
cout << sum << "\n";
}
}
return 0;
}